Precision Errors In Javascript

Recently I have posted a poll 🎙📟 in linkedin
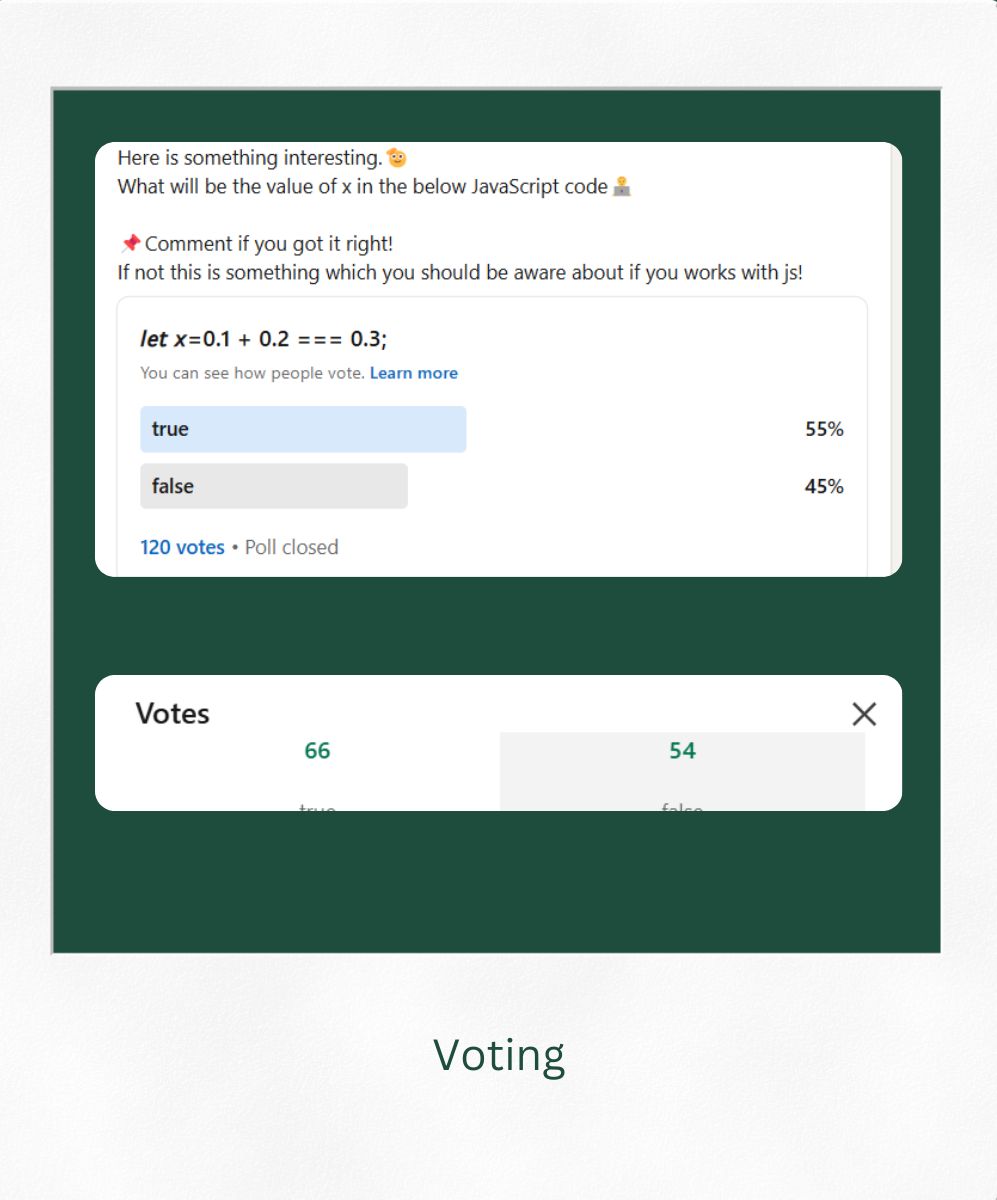
𝘞𝘩𝘢𝘵 𝘸𝘪𝘭𝘭 𝘣𝘦 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘷𝘢𝘭𝘶𝘦 𝘰𝘧 𝘹 𝘪𝘯 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘣𝘦𝘭𝘰𝘸 𝘑𝘢𝘷𝘢𝘚𝘤𝘳𝘪𝘱𝘵 𝘤𝘰𝘥𝘦👨💻
𝘭𝘦𝘵 𝘹=0.1 + 0.2 === 0.3;Even though mathematically this is true, In JavaScript x will be evaluated as false. Majority(66/120) of the people voted for wrong answer. This may be confusing for most of the people and good thing to be aware of! Here is why!📢
👉JavaScript (like many other programming languages) uses binary floating-point arithmetic (IEEE 754 standard), which can cause precision errors when representing certain decimal numbers. For example: 0.1 + 0.2 𝘳𝘦𝘴𝘶𝘭𝘵𝘴 𝘪𝘯 0.30000000000000004, 𝘯𝘰𝘵 𝘦𝘹𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘭𝘺 0.3.
👉You can handle this in below ways: 1️⃣𝘌𝘱𝘴𝘪𝘭𝘰𝘯 𝘊𝘰𝘮𝘱𝘢𝘳𝘪𝘴𝘰𝘯:Compare floating-point numbers in JavaScript, you can use a small threshold value called epsilon:
𝘔𝘢𝘵𝘩.𝘢𝘣𝘴(0.1+ 0.2- 0.3) < 𝘕𝘶𝘮𝘣𝘦𝘳.𝘌𝘗𝘚𝘐𝘓𝘖𝘕// 𝘵𝘳𝘶𝘦
▪This checks if the difference between the two numbers is within a very small range, effectively treating them as equal.
Read more about epsilon here
2️⃣𝘋𝘦𝘤𝘪𝘮𝘢𝘭 𝘓𝘪𝘣𝘳𝘢𝘳𝘪𝘦𝘴: Use libraries like BigDecimal.js or Big.js for exact decimal arithmetic when high precision is needed.
Here you can find more details on Number encoding
| Poll In Linkedin | Output From Console |
|---|---|
 |
 |
This Content was originally posted in linkedin View Post